
pDCPD Reaction Injection Molding (RIM) Provides Durability, Structural Advantages
November 30, 2016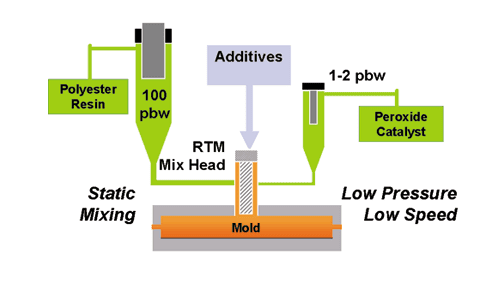
The Difference Between Thermoplastic and Thermosetting Plastic
May 15, 2017A Guide to the Resin Transfer Molding Process
In 1976, Osborne Industries, Inc., originated and initiated the closed-mold molding process that was later known in the plastics industry as resin transfer molding, or RTM. The resin transfer molding process has been in use ever since. RTM is one of the best methods for the mass production of composite parts. It is primarily used to mold components with large surface areas, complex shapes, and smooth finishes. The automotive, industrial equipment and agriculture industries have used the resin transfer molding process for decades for these reasons.
Below we discuss a more detailed step-by-step of the resin transfer molding process and its advantages.
1. Creating the Preform
The preform, or contoured fiberglass reinforcement, is the matrix, already in the shape of the finished product, into which the resin will be injected. First, the type of fiber must be defined. There are several different fiber types available for use in RTM composites, from random mats to two-dimensional woven rovings.
2. Preform Layup
Once the preform or fiberglass reinforcement is created, it is packed into a mold cavity that has the shape of the desired part.
3. Closing Mold
The mold cavity is then closed and clamped. The mold cavity allows for precise control over part thickness and allows for a smooth finish on both the A and B sides of the part. Gel coats may be used inside the mold to provide a high-quality, durable finish.
4. Injection Phase
Catalyzed, the low-viscosity resin is then pumped into the heated mold under pressure, displacing the air through vents , until the mold is filled. The injection phase must guarantee the complete impregnation of the preform. Bad impregnation of the fibers results in dry spot areas with missing adhesion between the layers.
5. Curing Phase
After the injection phase, the curing cycle starts, and the resin polymerizes to become rigid plastic. Curing time varies and is dependent on the mold temperature and chemistry of the resin being used.
Benefits of RTM
There are several benefits to using the resin transfer molding process over the alternative processes available. Some key benefits include:
- Good surface quality
- Wide range of reinforcements
- Large, complex shapes
- Dimensional tolerances
- Low capital investment
- Less material wastage
- Tooling flexibility
- Low environmental impact
- Labor savings
- Ability to add inserts and reinforcements at a point of infusion for greater strength
- Zero air entrapment within the product.
Resin transfer molding continues to be an increasingly popular method of fabrication. Contact Osborne Industries today for further information on how we can assist in your next molding project.


