What’s the Difference Between Monomers & Polymers?
September 17, 2018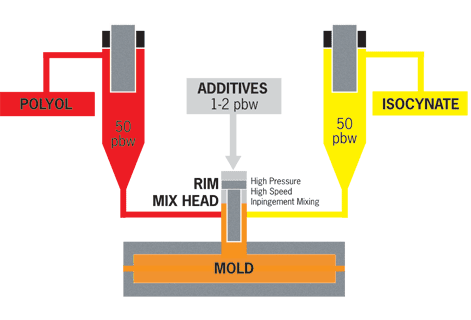
How Thermoset Plastics Are Made & Manufactured
December 6, 2018
The usefulness of gel coat vs paint for thermoset plastic parts is relative to the applications, needs, and requirements of the specific part. Gel coating is ideal and cost-effective for products produced via Resin Transfer Molding, because throughput is reduced when compared to a secondary painting process. However, if a part requires multiple colors or has a texture requirement, painting is a better alternative to gel coating. There are pros and cons to each. Here are a few for consideration.
Gel Coat
Gel coat is a thick, modified resin with colorants added. It is a durable, resilient, decorative surface found on plastic parts used for things like boats, bathtubs, vehicles, and the like. For the RTM process, gel coat can be applied as an in-mold coating. Gel coat is applied to molds in a liquid state, and once cured, produces a high-quality finish. The most common gel coats are made with thermosetting polymers, like polyester.
Thermoset plastics contain polymers that combine together during the curing process to form a permanent chemical bond. Once the thermosetting material hardens, it remain in a permanent solid state and can withstand high temperatures without losing its physical properties.
Pros
- Durable
- Minor scratches and blemishes can be sanded/buffed out
- Non-porous surface finish
- Easy to clean
- Long lasting
- Cost-effective on parts made with RTM
Cons
One disadvantage of gel coat is that it sometimes is difficult to color-match areas on a part if repair is necessary. Though scratches and blemishes can be sanded out due to its thickness, once done it sometimes requires an entire respray. Sanding and buffing may cause further discoloration to the underlying colors depending on the depth, especially if the underlying substrate is not pigmented to match the gel coat. However, at Osborne, the underlying polyester composite is always custom pigmented to match the gel coat, reducing the color differential if gel coat is damaged in the field.
- Difficult to repair
- Vulnerable to UV degradation without UV inhibitors
- Sanding/buffing can cause discoloration if underlying substrate is not pigmented to match
Paint
If gel coats work so effectively, why paint plastics in the first place? Resins used in in-mold gel coating offer a wide variety of colors. There’s no set answer, but one advantage of painting plastic parts is that paint offers a degree of customization not offered by gel coating.
Pros
In some instances, mass-produced products must be painted to meet certain specifications, needs, or requirements of a specific product color-scheme. Paint offers more texture options than those found in gel coats. Additionally, when paint is used on RTM-molded parts, the top coat can be matched to the paint on other parts—like metal—used on the end product. Color-fade over time would be uniform if all parts on the end product are painted, rather than mixing painted and gel-coated parts.
Plastic parts may also be painted by customers or by aftermarket refinishers for customization or repair.
- More flexible with color availability and matching
- Available in more textures
- Can be easily repainted
Cons
Painting plastic uses many of the same techniques as painting other types of materials. However, with regard to manufactured parts, its main disadvantage is time and money—painting costs more than gel coating. Paint thickness, hardness and adhesion are all important factors to consider when painting plastic parts. If applying paint post molding, to ensure a long-lasting quality finish, contaminants deposited during manufacturing must be removed first. Release agents injected with the plastic media in the mold often are contaminated and must be cleaned prior to painting, a step that adds to the cost.
For plastic parts that are exposed to the sun, both paint and gel-coats would need a UV inhibitor to slow fade and discoloration over time.
Be aware that some paints can also have significant effects that may compromise the mechanical properties of plastic parts. Paint’s properties are different than plastic, so the two must be compatible to work as a unit. Paint can be more brittle than the plastic substrate and can crack under stress, without affecting the substrate under similar conditions.
- Costs more time and money to apply
- May require multiple steps (cleaning, priming, painting)
- Has different properties than plastic and may be more brittle
Osborne Industries has over four decades of experience in thermoset plastic molding and utilizing gel coats and paint for a variety of parts. If you have questions about gel coat vs. paint for a thermoset plastic part, contact the experts at Osborne today!



