RIM Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step
February 16, 2018Top 3 Most Acid Resistant Plastics
April 20, 2018 Plastic is a synthetic material created from a broad range of organic polymers that have become an indispensable part of our everyday world. The properties of plastic are numerous. For the most part, they are:
Plastic is a synthetic material created from a broad range of organic polymers that have become an indispensable part of our everyday world. The properties of plastic are numerous. For the most part, they are:
- Lightweight with a high strength-to-weight ratio
- Can be manufactured inexpensively and mass produced
- Water resistant
- Shock resistant
- Thermally and electrically insulating
Metal vs Plastic
Compared to metal, plastic has a low melting point, is highly malleable, and can be molded easily into basic or complex forms. That malleability also increases the fabrication and production of parts and pieces. Unlike metals, finishes and colors can be added before fabrication and the need for certain post-treatment processes, such as painting. Finally, plastic does not rust. It is less susceptible and resistant to the kind of chemical reactions that affect metals like oxidation or rusting.
What is Plastic Used For?
Plastics vary as much as the many applications for it. We wear plastic in our clothes—polyester (PES) and polyamides (PA) (nylons). Our water and sewer delivery systems are made from it—polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The uses of polypropylene (PP) are seemingly endless. Packaging and labeling, carpeting, underwear, and jackets; stationery, plastic parts and recyclable containers of all kinds; laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, and many automotive parts are made from it. The list of polymers goes and on and on, e.g., polystyrene (PS), high impact polystyrene (HIPS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyurethane (PU), polycarbonate (PC) and polyethylene (PE).
Chemical Properties of Plastic
There are two primary forms of plastic: thermoplastic and thermoset plastics, the use of which is dependent on the application. The main physical difference between the two is that one can be reused time and again, and the other cannot. When thermoplastics are heated, there is no chemical bonding and the material’s physical properties remain unaffected. Thermoplastics then, can be molded, melted, and remolded repeatedly into various shapes, sizes, and objects.
Thermoset plastics are polymers similar to, but generally stronger than, thermoplastics because of the polymer’s molecular cross-linking. They are so named because the polymers experience a chemical change during processing to form an irreversible chemical bond when mixed and molded. Once formed and solidified, i.e., a process known as curing, the plastic becomes “set.” The transformation process from a liquid state to a solid state is irreversible and provides an ultra-strong end product. It cannot be melted or remolded and is resistant to solvents.
Thermoset molding compounds are designed for processes such as Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) and Reaction Injection Molding (RIM) with pDCPD (Polydicyclopentadiene), one of the more impact-resistant plastics available.
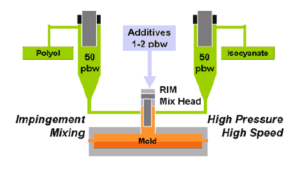
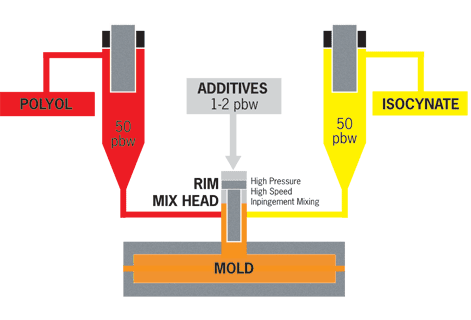
The RIM manufacturing process is a technique that utilizes engineered thermoset polymers. Low-viscosity liquid reacts chemically during the molding. The polymers expand, thicken, and harden after injection, and must be cured there. This allows for many more intricate designs than ordinary injection molding. And because of the lower viscosity liquid polymers used in molding thermosets than those in molten thermoplastic polymers, RIM molding techniques can produce high impact, heat resistant, light-weight, larger, stronger, and rust and corrosion-proof products like automotive bumpers and fenders, large truck and bus body parts, air spoilers, agricultural equipment, septic tanks, chlorine generation components, and much more.
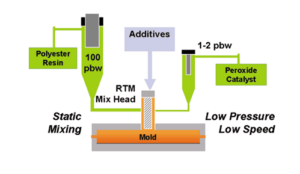 The RTM manufacturing process is similar to the RIM process but involves the injection of a low-viscosity thermoset into a closed mold under moderate pressure, approximately 5 psi, from one or more injection ports. A resin is mixed with a catalyst which acts as a hardener, and injected into a mold that contains dry fibers, such as fiberglass. The injected resin fills all the voids in the mold, reinforces the fiber types, and forms, usually within minutes. The result is heat, corrosion, abrasion, and impact-resistant material parts, which are utilized in the agricultural, aerospace, and transportation sectors, among others.
The RTM manufacturing process is similar to the RIM process but involves the injection of a low-viscosity thermoset into a closed mold under moderate pressure, approximately 5 psi, from one or more injection ports. A resin is mixed with a catalyst which acts as a hardener, and injected into a mold that contains dry fibers, such as fiberglass. The injected resin fills all the voids in the mold, reinforces the fiber types, and forms, usually within minutes. The result is heat, corrosion, abrasion, and impact-resistant material parts, which are utilized in the agricultural, aerospace, and transportation sectors, among others.
Thermoset Plastic Molding with Osborne Industries
Osborne Industries specialize in the production of RTM and RIM thermoset parts, with over 35 years of practical day-to-day production experience. Whatever the manufacturing needs of your company or industry, Osborne Industries will meet the challenges of the most complex plastics. Contact us today to get started!




